Section 18: Network Requests - Sending Http Requests via JavaScript

The goals
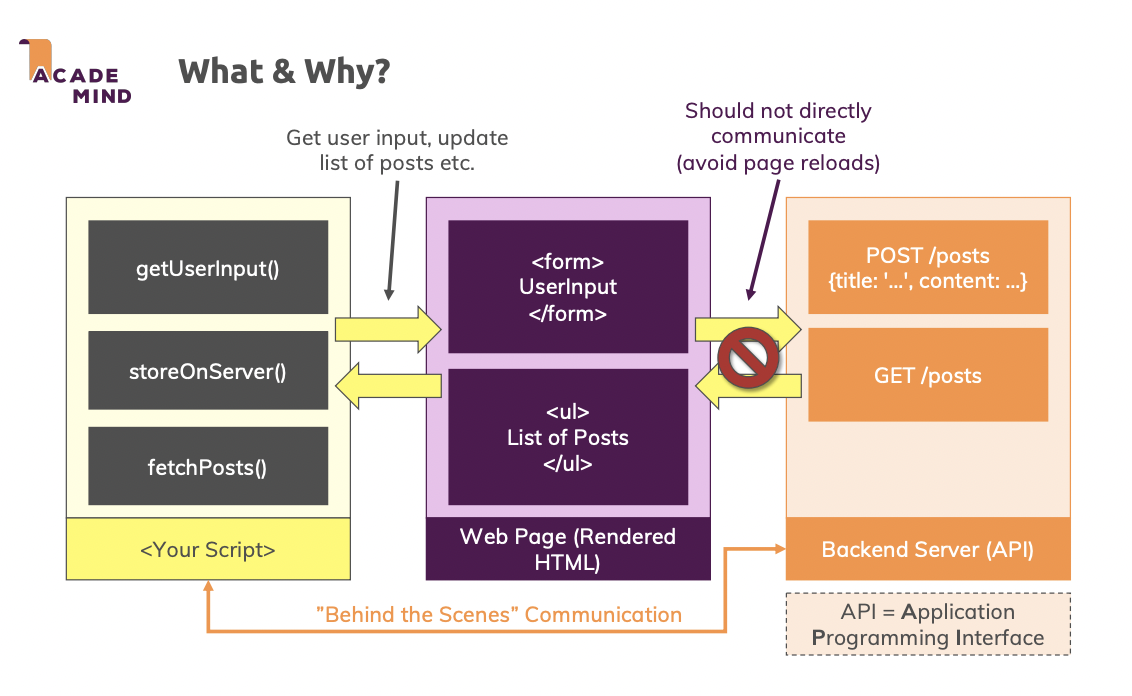
💪🏻What & Why?
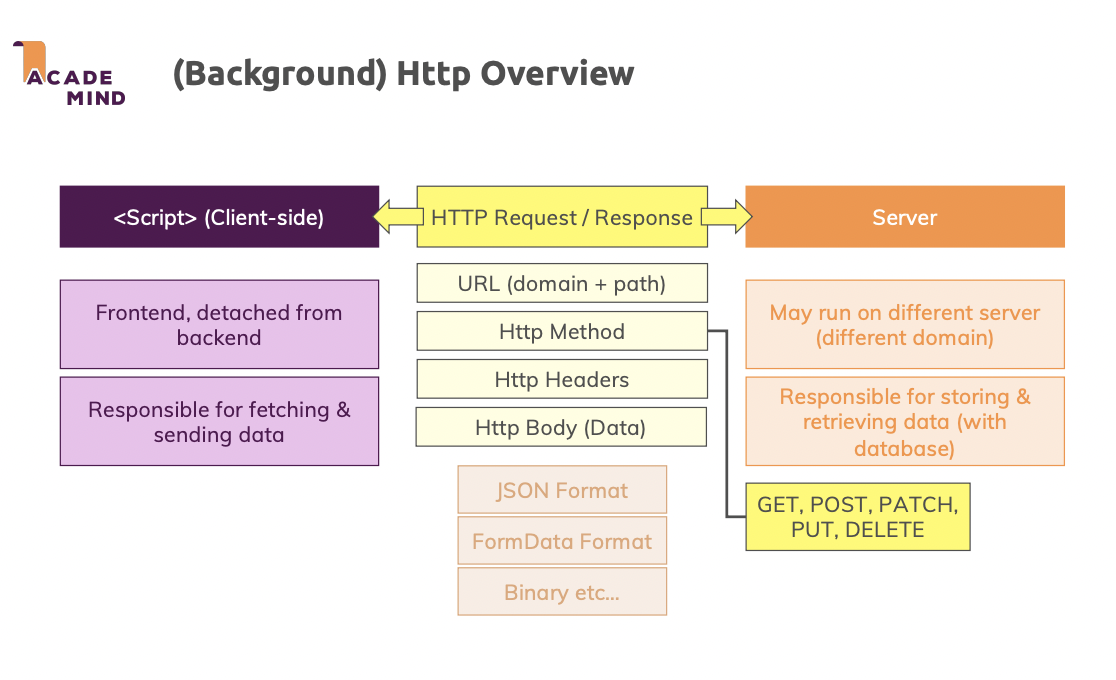
✌🏻XMLHttpRequest & fetch() API
👍🏻JSON Data & FormData
👊🏻GETting Data, POSTing Data
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts');
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.onload = function() {
// const listOfPosts = JSON.parse(xhr.response);
// we can do like this but there is another simple way
const listOfPosts = xhr.response;
// console.log(xhr.response);
// json type so we can't use it as like array
}
xhr.send()
JSON 데이터 파헤치기
일반적으로 데이터는 클라이언트 측 코드와 백엔드("서버") 사이에서 "JSON" 데이터로 전송됩니다.
JSON은 JavaScript Object Notation의 약자로, 아래와 같습니다.
{
"name": "Max",
"age": 30,
"hobbies": [
{ "id": "h1", "title": "Sports" },
{ "id": "h2", "title": "Cooking" }
],
"isInstructor": true
}JSON 데이터는 객체({}), 배열([]), 문자열(반드시 큰 따옴표 사용!), 숫자(따옴표 없이)와 불리언(따옴표 없이)을 지원합니다.
모든 객체 키(예: "name")는 큰 따옴표로 묶어야 합니다. 따옴표가 없는 경우나 작은 따옴표의 경우는 허용되지 않습니다!!
모든 JSON “객체”는 따옴표로 묶입니다. 결국에는 JSON 데이터가 위에 표시된 형식의 데이터를 포함하는 문자열이기 때문입니다.
여러분이 직접 테스트해볼 수 있습니다 - 다음 JSON JavaScript가 아닌 객체를 가져와서 JSON.stringify()를 적용해 보세요. 그러면 JSON 데이터로 변환됩니다. 개발 도구 콘솔에서 그렇게 하면 결국 위에서 살펴본 대로 형식이 지정된 데이터가 포함된 문자열을 얻게 됩니다.
const person = { // 이것은 JSON이 아닙니다 - 일반("날 것의") JavaScript 객체입니다!
name: 'Max',
age: 30,
hobbies: [
{ id: 'h1', title: 'Sports' },
{ id: 'h2', title: 'Cooking' }
],
isInstructor: true
};
const jsonData = JSON.stringify(person); // JS 데이터를 JSON 데이터 문자열로 변환
console.log(jsonData); // 컴퓨터가 읽을 수 있는 JSON 데이터가 포함된 문자열
console.log(typeof jsonData); // string기계에 대한 구문 분석이 쉽고 사람이 읽기에도 나쁘지 않기 때문에 JSON 데이터를 사용합니다.
JSON 데이터를 수신하고 이를 다시 일반 JS 데이터로 변환하려는 경우 JSON.parse()를 사용할 수 있습니다:
const parsedData = JSON.parse(jsonData);
// yields a "raw" JS object/ array etc.알아두면 좋은 정보. 데이터를 JSON으로 변환할 수 있는 것은 객체로 제한되지 않습니다. 숫자, 배열, 불리언 또는 문자열도 변환할 수도 있습니다 - JSON이 지원하는 모든 데이터 유형이 변환 가능합니다.
const jsonNumber = JSON.stringify(2); // "2"
const jsonText = JSON.stringify('Hi there! I use single quotes in raw JS'); // ""Hi there! ...""
const jsonArray = JSON.stringify([1, 2, 3]); // "[1,2,3]"
const jsonBoolean = JSON.stringify(true); // "true"
다음은 혼선을 막기 위한 간단한 메모입니다. 데모 애플리케이션에서 "Fetch" 버튼은 항상 기존 데이터를 먼저 지우지 않고 데이터를 추가합니다. 즉 버튼을 여러 번 누르면 더 많은 항목이 계속 추가됩니다.
물론 먼저 내용을 지우고 추가하도록 코드를 조정할 수도 있습니다.
function sendHttpRequest(method, url, data) {
// const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
// xhr.open(method, url);
// xhr.responseType = 'json';
// xhr.onload = function() {
// if (xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300) {
// resolve(xhr.response);
// } else {
// xhr.response;
// reject(new Error('Something went wrong!'));
// }
// // const listOfPosts = JSON.parse(xhr.response);
// };
// xhr.onerror = function() {
// reject(new Error('Failed to send request!'));
// };
// xhr.send(JSON.stringify(data));
// });
// return promise;
return fetch(url, {
method: method,
// body: JSON.stringify(data),
body: data,
// headers: {
// 'Content-Type': 'application/json'
// }
})
.then(response => {
if (response.status >= 200 && response.status < 300) {
return response.json();
} else {
return response.json().then(errData => {
console.log(errData);
throw new Error('Something went wrong - server-side.');
});
}
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error);
throw new Error('Something went wrong!');
});
}1. fetch는 promise객체를 반환, 즉 따로 뭐 할 것 없이 바로 '.then', '.catch'등의 메소드 연결해서 사용 가능
2. 이 때 catch는 네트워크상에 큰 오류로 페이지가 셧다운되지 않는 이상은 에러를 캐치해내지 못하는데 이를 보완하기 위해 if문을 사용해서 status가 정상 (200, 202등의 경우)시에만 출력되도록 작성
formData
In JavaScript, a FormData object is a common way to create a bundle of data to send to the server using XMLHttpRequest or fetch.
It replicates the functionality of the HTML form element.
We can think of it as an array of arrays. There is one array for each element that we want to send to the server.
Each element consists of the following three things:
- name: The name of the field.
- value: The value of the field. It can be a String or Blob.
- filename: The file’s name to be saved on the server when a Blob is passed as the second parameter.
Syntax
const formData = new FormData([form]);
Parameter
The formData constructor creates and returns a new FormData object.
If an HTML form element is provided, it automatically captures its fields. This parameter is optional.
Additional data can be added in the FormData object using the formData.append() method.
formData.append(name, value, filename);The FormData interface provides a way to easily construct a set of key/value pairs representing form fields and their values, which can then be easily sent using the fetch() or XMLHttpRequest.send() method. It uses the same format a form would use if the encoding type were set to "multipart/form-data".
You can also pass it directly to the URLSearchParams constructor if you want to generate query parameters in the way a <form> would do if it were using simple GET submission.
An object implementing FormData can directly be used in a for...of structure, instead of entries(): for (const p of myFormData) is equivalent to for (const p of myFormData.entries()).
Sources
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/
JSONPlaceholder - Free Fake REST API
{JSON} Placeholder Free fake API for testing and prototyping. Powered by JSON Server + LowDB. Tested with XV. As of Oct 2022, serving ~1.7 billion requests each month.
jsonplaceholder.typicode.com
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/FormData
FormData - Web APIs | MDN
The FormData interface provides a way to easily construct a set of key/value pairs representing form fields and their values, which can then be easily sent using the fetch() or XMLHttpRequest.send() method. It uses the same format a form would use if the e
developer.mozilla.org
https://www.educative.io/answers/what-is-a-formdata-object-in-javascript
What is a formData Object in JavaScript?
Contributor: Shubham Singh Kshatriya
www.educative.io